Commons:Hranice originality
Shortcuts: COM:TO • COM:TOO • COM:THRESHOLD
Hranice originality je koncept v autorském zákoně, který se používá k posouzení, zda konkrétní výtvor nebo jeho část může být stále chráněna autorským zákonem. Používá se k rozlišení výtvorů, které jsou dostatečně originální k ochraně autorským zákonem od těch, které nejsou. V tomto kontextu, „originalita“ označuje „pocházející od někoho jako původce/autor“ (jelikož to jaksi promítá osobnost autora), místo „nikdy se to neobjevilo nebo nikdy neexistovalo“ (což by evokovalo ochranu něčeho nového, jako se děje v ochraně patentem).
Je pravidlem, že autorský zákon se vztahuje na výtvor jako celek. Pokud výtvor obsahuje část, která je dostatečně složitá k ochraně autorským zákonem, potom celý výtvor je považován za chráněný autorským zákonem. Nikdo takový výtvor nesmí nahrát na Commons s aplikací pravidla de minimis na část, která není triviální.
Zbytek této stránky se věnuje obrázkům shledanými nedostatečnými pro ochranu autorským zákonem soudem či jinou autoritou. Většinou nelze posoudit, zda konkrétní obrázek je v rámci hranice originality bez soudního rozhodnutí. Nicméně, dle principu prevence by obrázek měl být smazán, pokud jsou zde silné pochybnosti o tom, zda obrázek skutečně není autorsky chráněn.
Pro více informací viz Hranice originality na Wikipedii.

Mapa
- [This illustration is not explained enough. You may edit the page to make it clearer.]
COM:TOO United States
Nejsou k dispozici žádné informace
Země s civilními zákony
Země s civilními zákony většinou vyžadují relativně vysokou minimální hladinu intelektuální kreaticity, která vyloučí obyčejné podpisy a jednoduchá loga z autorské ochrany. Nicméně to stále neplatí pro všechny takové země. Například Rakousko a Čína jsou obě známé relativně nízkou hranicí originality.
Pokud víte o specifickém případu zákona či právní rady o této problematice v jakékoliv zemi, prosíme, přidejte sekci „Hranice originality“ do příslušné podstránky země v Commons:Autorská práva podle oblastí a přidejte odkaz do příspěvku níže.
COM:TOO Afghanistan
Afghánistán
According to the 2008 Copyright Law, work that may be protected includes: Photography work that has been created using an innovative mode; Innovative work of handicraft or industrial art (carpet designs, rugs, felt carpet and its attachments etc.); Innovative work which has been created based on the public culture (folklore) or national cultural heritage and art.[2008 Article 6(1) items 7-9]
COM:TOO Austria
Rakousko
Austria has a low threshold of originality despite being a civil law country. See the archived discussion on the German Wikipedia.
These logos are ![]() :
:
COM:TOO Brazil
Brazílie
There are some court cases related to threshold of originality in Brazil. According to one study, and the court decisions contained in it, the concept of creativity in Brazil is way more strict and exigent than in the United States, and consequently the threshold of originality is considerably higher than the United States, which is the general reference in Commons.[5]
Examples:
 . In the case of Boneco de Preço Miúdo (2011), puppets that were a tridimensional and humanized version of a logo were deemed by the court to lack enough originality to be protected. The court considered that there was no originality or unpublished work in the puppets because they represented an already existing symbol (the supermarket's logo), and that there were already previous 3D and humanized versions of that logo. The court did not grant any value nor legal protection to the specific 3D and humanized version of the logo in question, and called it something like a "stylization subordinate to a previous idea".[6]
. In the case of Boneco de Preço Miúdo (2011), puppets that were a tridimensional and humanized version of a logo were deemed by the court to lack enough originality to be protected. The court considered that there was no originality or unpublished work in the puppets because they represented an already existing symbol (the supermarket's logo), and that there were already previous 3D and humanized versions of that logo. The court did not grant any value nor legal protection to the specific 3D and humanized version of the logo in question, and called it something like a "stylization subordinate to a previous idea".[6] . Copyright for compilations/ reorganizations of already existing elements has often been rejected on court, hinting that the threshold for what constitutes an "intellectual creation" in this respect is quite high in Brazil.[7]
. Copyright for compilations/ reorganizations of already existing elements has often been rejected on court, hinting that the threshold for what constitutes an "intellectual creation" in this respect is quite high in Brazil.[7] . Slogans are generally acceptable. In rare occasions they may be protected, when there is such a level of creativity as to attain the level of a literary work. For example, in the Guerra das Moedas court case (2013), copyright in the expression was not recognized by the court. The verdict stated that the language is the cultural patrimony of the people, so language expressions can't be protected by law. The Rede Globo vs. Ronaldo Ciambroni case was similar.[8][9]
. Slogans are generally acceptable. In rare occasions they may be protected, when there is such a level of creativity as to attain the level of a literary work. For example, in the Guerra das Moedas court case (2013), copyright in the expression was not recognized by the court. The verdict stated that the language is the cultural patrimony of the people, so language expressions can't be protected by law. The Rede Globo vs. Ronaldo Ciambroni case was similar.[8][9]
Some examples help define which photos are, and are not, "artistic creations", and therefore object of protection under the 1973 copyright law:
 . The facade of the Jung Frau building, in Joinville, as well as partial views of the city, when photographed in an obvious simple way, without employment of any special ("diferenciada") technique". The court ruled: "photographs are not considered artistic creations ... that portray in a manifestly simple way, without use of any differentiated technique, the front of a residential building and a partial view of the city, under a service contract with a real estate business with a predefined advertising purpose"[10]
. The facade of the Jung Frau building, in Joinville, as well as partial views of the city, when photographed in an obvious simple way, without employment of any special ("diferenciada") technique". The court ruled: "photographs are not considered artistic creations ... that portray in a manifestly simple way, without use of any differentiated technique, the front of a residential building and a partial view of the city, under a service contract with a real estate business with a predefined advertising purpose"[10] . Simple documentary, descriptive photographs in general, such as photographs documenting social reunions: In SC-AC 111630 SC 2002.011163-0 (2006): "mere photographic documentation, without artistic character, does not qualify for copyright ... making it possible to use a copy without mention of the photographer's name, since, according to Brazilian law, only artistic photography (by choice of the object and conditions of execution) is listed among protected works. ... [for example] with documentary photographs of social gatherings, where the author was performing duties for the defendant, a reference to the photographer's name is not required because it is not an artistic work..."[11]
. Simple documentary, descriptive photographs in general, such as photographs documenting social reunions: In SC-AC 111630 SC 2002.011163-0 (2006): "mere photographic documentation, without artistic character, does not qualify for copyright ... making it possible to use a copy without mention of the photographer's name, since, according to Brazilian law, only artistic photography (by choice of the object and conditions of execution) is listed among protected works. ... [for example] with documentary photographs of social gatherings, where the author was performing duties for the defendant, a reference to the photographer's name is not required because it is not an artistic work..."[11] . A 2000 ruling stated: "Photographs for identity documents, produced by automatic machines, are not artistic works. ... Neither should purely technical photographs, which reproduce a certain object without the slightest artistic concern, be protected by copyright."[12]
. A 2000 ruling stated: "Photographs for identity documents, produced by automatic machines, are not artistic works. ... Neither should purely technical photographs, which reproduce a certain object without the slightest artistic concern, be protected by copyright."[12] Another 2000 decision stated: "the photos [...] have an artistic character characterized by the originality, creativity and technique of its author, elements that reveal ... a work of art. They are not, as the appellant claims, mere reproductions of images for advertising purposes, or common snapshots."[13]
Another 2000 decision stated: "the photos [...] have an artistic character characterized by the originality, creativity and technique of its author, elements that reveal ... a work of art. They are not, as the appellant claims, mere reproductions of images for advertising purposes, or common snapshots."[13]
![]() Puppets who were a tridimensional and humanized version of this logo were deemed in court to lack enough originality to be protected.
Puppets who were a tridimensional and humanized version of this logo were deemed in court to lack enough originality to be protected.
COM:TOO Czech Republic
Česko
Dílo musí být „jedinečným výsledkem tvůrčí činnosti autora“.[121/2000-2006 čl. 2 odst. 1] U fotografií a počítačových programů stačí, když je dílo „původní v tom smyslu, že je autorovým vlastním duševním výtvorem“.[121/2000-2006 čl. 2 odst. 2]
COM:TOO Chile
Chile
Registration in the Intellectual Property Registry generates a "presumption" of copyright in favor of the registrant. Any work may be registered for "presumed" copyright, but Law No. 17.336 clearly states the "presumed" copyright may be contested.
COM:TOO China
Čína
China has a relatively low threshold of originality standard; basic designs may be copyrightable. One of the most noticeable cases is the logo of a company named Gang Heng (listed below) ruled by China's supreme court as copyrighted (see below).
The following examples are ![]() :
:
- "Matchstick man" (image) with a black sphere as a head, black lines as torso, limbs and feet is not copyrightable for lacking originality, ruled Higher People's Court of Beijing Municipality (source).
- Five SKECHERS logos (image) are not copyrightable for lacking originality, ruled Higher People's Court of Beijing Municipality in 2020 (final judgement and related news coverage).
- "BIOU" logo (image), with letter "b" and "o", and a small barcode in the upper right corner, is not copyrightable for lacking originality, ruled Higher People's Court of Beijing Municipality in 2018 (final judgement and related articles [1] [2]). Note that the logo was initially ruled as copyrightable by the Trademark Review and Adjudication Board and a lower court.
- "KON" logo (see below), with three black bars crossed together, is not copyrightable for lacking originality, ruled Beijing Dongcheng District People's Court in 2019 (final judgement and news coverage).
- "Chao Qun" logo (see below), is not copyrightable for lacking originality, ruled China's Supreme People's Court in 2012 (original judgment by the Court). The court asserted that the expression does not show the existence of a unique style; there are only subtle differences when compared to the common Seal script and Clerical script, the "Chao Qun" logo does not reach a certain creative height, and does not have originality.
-
A stick figure similar to this image, where the head is represented by a circle and other parts represented by straight lines, is not copyrightable.
-
The SKECHERS's S logo is not copyrightable.
-
KON logo with three black bars crossed together is not copyrightable.
-
Chao Qun logo is not copyrightable.
The following examples are ![]() Not OK:
Not OK:
- Calligraphy works, such as:
- the work "道" on this photo (archived from original) (see the article by Beijing Youth Daily (archived from original), and the follow-up report (archived from original).
- the character "勁" (archived from the original), with rulings made by Beijing No.1 Intermediate People's Court, and Higher People's Court of Beijing Municipality
- calligraphy for "澳門豆撈" (image), ruled by Henan Zhengzhou Intermediate People's Court (source).
- are copyrighted (Copyright Law of the PR China: "Article 2 Works of Chinese citizens, legal entities or other organizations, whether published or not, shall enjoy copyright in accordance with this Law." ; "Article 3 'Works' mentioned in this Law shall include [...] in the following forms: (4) works of fine art and architecture" ; Regulations for the Implementation: "Article 4 (8) 'works of fine arts' means [...] such as paintings, works of calligraphy and sculptures;")
- Handwriting: a hand-written manuscript was deemed copyrightable as work of art, according to a decision made by Nanjing Intermediate People's Court in 2017 (sources: [3] [4], Final judgement).
- "LY" company logo (alternative link; archived from the original), although arguably relatively simple, has been ruled copyrightable by Trademark Appeal Board of the State Administration of Industry & Commerce, Beijing Intellectual Property Court, and Higher People's Court of Beijing Municipality.
- Typefaces of characters "笑", "喜", and "城市宝贝" in these two logos are copyrightable, ruled Nanjing Intermediate People's Court in 2012. However the character "巴" in the same logo was decided not copyrightable for lacking originality in the same decision. (source, court decision full text: Final judgement)
- Gang Heng logo: China's Supreme People's Court ruled this logo to be protected by copyright in 2014 (original judgment by the Court; related news coverage).
- Dyneema logo (in this article): China's Supreme People's Court ruled this logo to be protected by copyright in 2017 (original judgment by the Court).
- K2 Sports logo as shown in the image below is eligible for copyright protection, determined during trademark adjudication proceedings in 2010 (source).
-
The logo of K2 Sports is copyrightable in China (but not copyrightable in its country of origin, the US).
- The CamScanner logo (国作登字-2021-F-00062063).
COM:TOO Denmark
Dánsko
| Status | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|
 |
Three fonts not eligible for copyright protection (Supreme Court 30 June 2006, U2006.2697H). Two other fonts were found eligible for copyright. | |
 |
Sketches of windows and doors not eligible for copyright protection (The Maritime and Commercial Court 8 August 2003.)[14][15] | |
_01.jpg/100px-WWF_Schweiz%2C_Zürich_Office_(Ank_Kumar%2C_Infosys_Limited)_01.jpg) |
The WWF panda logo is not protected by copyright[16] | |
 |
The GLOBAL knife design is copyright protected in Denmark.[17] | |
 |
A specific chair design (Tripp Trapp).[18] |
COM:TOO Finland
Finsko
For works of visual art, the threshold of originality is relatively low.[19]
Simple logos, however, are generally below the threshold of originality.[20] In particular, the threshold is high when only basic colors and shapes (such as triangles, squares and circles or capital letters) are used.[21][19]
 |
Simple photograph with limited copyright period – not a photographic work of art. (TN 2003:6) | |
 |
Differences compared to the coat of arms of the historic region did not meet threshold of originality. (TN 1998:5) | |
| Commons:Deletion_requests/Aalto_vases | "The wave-like forms of the [original Aalto vases] do not... result from the intended use of the object but the creative mental effort of the author. [Therefore the original vases] are independent and original enough to be considered works of art as meant in 1 § of [the Finnish Copyright law]" (p. 4). (TN 2010:10) | |
| A specific house type | (Eurohouse S 2, court ruling) | |
| The logo is below the threshold of originality because it is "ordinary and [does] not express an independent and original result of a creative process of its author. Somebody else in undertaking a comparable task could have contrived a similar ... logo". (TN 2000:1) | ||
| Save the Children Fund logo | The logo is above the threshold of originality, because its "visual manifestation is the creative work of its author, whereby the ideological basis of the fund has been successfully conformed with in an independent and original manner... [N]o one else undertaking a comparable task could have reached a similar outcome". (TN 2010:3) | |
and |
The logos are "in their literary and visual manifestation simple and ordinary to the degree that they are not to be regarded as original works in their own regard." (TN 2009:2) | |
| The logo is "is not original and independent in such a way that it would be protected ... by copyright". (TN 2011:7) | ||
| The logo is below the threshold of originality because "its central elements and the way in which they have been combined are commonly used in logos and are thus ordinary". (TN 2000:1) | ||
| "Silmu" logo | Although the logo consists of a "stylized, albeit fairly simple, red tulip", it is above the threshold of originality for works of visual art. (TN 2001:12) |
COM:TOO France
Francie
French law asserts that a work is copyrightable when it bears the "imprint of the personality of the author". In practice, it depends on the work in question, but this has left the bar quite low for many works where an artistic intent can be shown. For an art exhibition, a man placed the word paradis with gold lettering above the bathroom door of the old dormitory of alcoholics at a psychiatric facility, and termed it artwork; the French courts agreed with him that it was copyrightable based on the aesthetic choices made ("affixing the word 'paradise' in gold with patina effect and a special graphics on dilapidated door, the lock-shaped cross, encased in a crumbling wall with peeling paint").[22]
France has "a slightly higher threshold of originality in general, and particularly so in the context of photographic works".[23]
A decision from Supreme court (Cour de Cassation) on October 2011 agreed with appeal court decision saying that a quite artistic picture of two fish on a yellow plate about a traditional Marseille meal could not be protected by French law because of lack of originality.[24] According to this decision, level of originality required by this appeal court is very high. This decision was criticized but French supreme court does not control facts but only controls interpretation of the law. In 2017, copyright protection on this image of Jimi Hendrix was restored after a court initially denied protection.
COM:TOO Germany
Německo
Nejsou k dispozici žádné informace
COM:TOO Greece
Řecko
The term “work” is defined as including any original intellectual creation expressed in any form, including alterations of other works as well as collections of works, provided that the selection or the arrangement of such collections is original.[25]
Originality is understood by Greek jurisprudence as a notion of “statistical uniqueness”, which means that the work involves skill, labor and judgment emanating from the author and that no other person, acting under the same circumstances, could produce the exact same work.[26]
COM:TOO Hungary
Maďarsko
![]()
- stylized text with a common stylized globe icon (does not show the actual image).[27]
![]()
COM:TOO Indonesia
Indonésie
Indonesia's threshold of originality is reportedly low, being based on common law ("Anglo-American model") principles, with "wallpaper, wrappers, packaging designs and technical drawings" being registered by copyright authorities.[29]
COM:TOO Iran
Írán
![]() for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection in Iran seems very low.
for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection in Iran seems very low.
The following are registrable for copyright protection: "(...) pictures, drawings, designs, decorative writings, (...) or any decorative and imaginative work produced in any simple or complex manner "
COM:TOO Italy
Itálie
Hogan Lovells states "In summary, the threshold for an industrial design product to enjoy copyright protection is still quite high and even famous industrial design products have been denied such protection by Italian Courts."[30]
Probably this applies to logos too. These files have been kept as simple logos:
But the logo of AC Parma was deleted as being a complex logo.[31] Another Parma logo has been deleted but then restored.
COM:TOO Japan
Japonsko
Logos in the gallery below are ![]() to upload.
to upload.
Article 2 of Japanese copyright law defines that a work is eligible for copyright when it is a production in which thoughts or sentiments are expressed in a creative way and which falls within the literary, scientific, artistic or musical domain.[32]
Japanese courts have decided that to be copyrightable, a text logo needs to have artistic appearance that is worth artistic appreciation. Logos composed merely of geometric shapes and texts are also not copyrightable in general.

|
(DR) Tokyo High Court's ruling: letters are a means of communication, shared by all. Copyright protection of fonts is limited only to those that raise artistic appreciation as much as artistic works do.[33] |

|
(DR) Tokyo High Court's ruling: although the shape is stylized, the text is in a normal arrangement and keeps its function of being read as a sequence of letters.[34] |

|
Tokyo District Court's ruling: the Court is negative towards recognizing the symbol as a copyrightable work of fine arts, because it is considered merely relatively simple graphic elements.[35] |
- Furby toy: utilitarian, so not protected by copyright as an artistic work. Not utilitarian in the United States, so photos of the toy can't be uploaded to Commons.[36]
COM:TOO Libya
Libye
For photographic and cinematic works which are limited to the mere mechanical transmission of scenery, rights expire 5 years from the date of first publication.[9/1968 Article 20]
COM:TOO Luxembourg
Lucembursko
According to Jean-Luc Putz, the threshold of originality in Luxembourg is not as strict as in UK but not as liberal as in Germany. During the legislation the intent was to orientate with other Benelux states or France.[37]
COM:TOO Mexico
Mexiko
As indicated above, the following are examples of what is and what is not protected under the 1996 copyright law:
- These images are
 to upload to Commons
to upload to Commons
-
Letters, digits or isolated colors
-
Names and titles or isolated phrases
-
Simple formats or blank forms to be filled with any type of information, as well as their instructions (example picture)
-
Reproductions or imitations, without authorization, of shields, flags or emblems of any country, state, municipality or equivalent political division
-
Reproductions or imitations, without authorization, of international governmental, non-governmental organizations, or of any other officially recognized organization
- These are
 to upload to Commons (unless published under a free license by the copyright holder), because they are above the threshold of originality required for copyright protection and are not covered by the law itself.
to upload to Commons (unless published under a free license by the copyright holder), because they are above the threshold of originality required for copyright protection and are not covered by the law itself.
COM:TOO Netherlands
Nizozemsko
Simple logos are okay in the Netherlands but not all logos are. Whether something is above the threshold of originality in the Netherlands is defined in the Supreme Court judgment "'Van Dale/Romme'". In this judgment, the Supreme Court ruled that:[38]
- In assessing the ground of cassation it should be noted that, for a product to be considered a work of literature, science or art as meant in article 1 in conjunction with article 10 of the Copyright law (Auteurswet), it is required that it has an own, original character and bears the personal mark of the maker.
This was further specified in the Supreme Court judgment ''Endstra-tapes':[39]
- The product has to bear an own, original character. In short, this means the shape may not be based on that of another work. (cf. article 13 Aw.) The demand that the product has to bear the personal mark of the maker means that there has to be a shape that is the result of creative human labor and thus creative choices, which therefore is a product of the human mind. In any case, excluded from this is everything that has a shape that is so trivial or banal, that one cannot show any creative labor behind it of any kind whatsoever.
Later the Supreme Court determined in judgment on Stokke v. Fikszo that:[40]
- For a work to be eligible for copyright, it is necessary that the work has an own original character and bears the personal mark of the maker ... The Court of Justice of the European Union has has formulated the benchmark in such a way that it must concern "an intellectual creation of the author of the work".
COM:TOO Norway
Norsko
- Not protected
Two-minute theatre play.[41]
- Protected
- A specific chair design (Tripp Trapp)
- The logo for the TV series Jul i Blåfjell.[42]
COM:TOO Peru
Peru
Indecopi established parameters to qualify the originality of graphic and photographic compositions. Because of the higher originality threshold (independent of its endeavour, novelty, inspiration and technique, the requirement is to leave some space for the development of its author's personality, not a copy or imitation, referred as "originalidad subjetiva"),[43] simple designs, non-production videographic creations and old photographs without demonstrating their individuality can be uploaded to Commons. See also Andean Community: Threshold of originality.
Simple photographs
Old published photographs have a copyright term of 20 years counted from the first of January of the year following that of the disclosing of the photograph before 1976. The notes shown are based on the rescinded 1961 law:
- For old pictures taken prior to 31 December 1975 and which were not published within an author's own work
 fail to meet the general definition of a "work" under 1961 law (and Article 3.4 of Universal Copyright Convention: "The provisions […] not apply to photographic works […] shall not be less than ten years").[44] The duration of the photograph was for 20 years after performed its first copy, without the author presenting this in a literary, scientific or documentary work, from January 1 of the following year.[13714/1961 Art. 27] They were not renewed during the URAA date.[13714/1961 Art. 27 and 57] Use {{PD-Peru-photo}}.
fail to meet the general definition of a "work" under 1961 law (and Article 3.4 of Universal Copyright Convention: "The provisions […] not apply to photographic works […] shall not be less than ten years").[44] The duration of the photograph was for 20 years after performed its first copy, without the author presenting this in a literary, scientific or documentary work, from January 1 of the following year.[13714/1961 Art. 27] They were not renewed during the URAA date.[13714/1961 Art. 27 and 57] Use {{PD-Peru-photo}}. - The duration is reduced if the following occurs: when the author did not place the name of the label with the message "Reproduction prohibited" or that the author published in a work without a full name or under an unknown pseudonym.[13714/1961 Art. 58] The duration of anonymous works prior to 31 December 1980 was 15 years after publication and expired on 1 January 1996. They were not renewed during the URAA date. Use {{PD-Peru-anonymous}}.
- If they were used in literary or scientific works, they were documentary works or are reproductions of artistic material "of private domain", and the author died before 1946 (of before 1966 if someone had no family heirs), the law considers the photographs as
 the author's work (life + 30/50 years).[44] In the case of collective works, the date is considered to be the last survivor. If they died after 1947, they are protected by the current law. Use {{PD-Peru-1961law}}.
the author's work (life + 30/50 years).[44] In the case of collective works, the date is considered to be the last survivor. If they died after 1947, they are protected by the current law. Use {{PD-Peru-1961law}}.
Recent published photographs below threshold have a copyright term of 70 years counted from the first of January of the year following that of the taking of the photograph. Fortunately, this term usually flexible in the cases and facts shown below:
- The general definition of a "work" in the 1996 law is "any personal and original intellectual creation capable of being disclosed or reproduced in any form that is or may yet become known".[822/1996 Art.2(17)] Simple photographs taken or disclosed since 1976 are those which
 fail to meet the general definition of a "work" and only receive neighbouring rights,[822/1996 Art.144] but works above this threshold
fail to meet the general definition of a "work" and only receive neighbouring rights,[822/1996 Art.144] but works above this threshold  will receive standard protection (life + 70 years, see below).
will receive standard protection (life + 70 years, see below). - The Court of Indecopi believes that originality in a photograph should be limited to the originality of any work, requirements to protect against plagiarism. According to article 3.c of the Regulation of Inscriptions in the Registry National Copyright Act, provides that "no may be subject to registration the photographs that are limited to simple reproductions of people, of things, or of objects already existing or showing a mere documentary character [...] photography to be a work can not constitute only a simple reproduction of already existing objects".[45]
- Derecho PUCP journal explains examples of highly distinguishable events that surpass the threshold of originality: creative use of lights, unique moment, transmission of a message in their work and the photographer's personality. Below these and other criteria, simple photographs are legislated under Legislative Decree 1044 on unfair competition.[46]
Examples for photographs under 1961 law:
-
Photography within an advertisement not considered "literary work". Image protection expired in 1988. It also can't be protected in the 1996 law. See UR.
-
Photography taken in 1973 for a sports magazine. Because this is a journalistic assignment for an organization, the photograph remained protected for 20 years until its expiration in 1993. It also can't be protected in the 1996 law. See DR.
Examples for photographs under 1996 law:
- In 2002 the Court considered two images of household appliances as below of threshold of originality due to the lack of creative evidence, despite they are in a catalog with individuality. See Resolution No 354-2002/TPI-INDECOPI.[47]
- Also, in 2002 the Court ruled that a magazine photograph of Skándalo boy band in ordinary dress and solid-colored background receives related rights-only because it lacks individuality. See Resolution No 378-2002/TPI-INDECOPI, Alomi Producciones S.A.C. v Karinto S.A p.13.[45]
- In 2007 the Court justified a photograph of gift box for a web catalog as original work because of its shade selection and during the editing process it carried meticulous details, specifically the colored shade artificially created. See Resolution No 1263-2007/TPI-INDECOPI, Enrique Capella v Grupo Americano de Comercio S.A.C. and Citybank del Perú S.A p.4.[48]
- In 2008 the court determined that press snapshots of sporting, political or weather events lack originality for lack of prior preparation in their production. See Resolution No 2521-2008/TPI-Indecopi, Agencia Efe S.A. v Las Rosas Editorial S.A.C.
- In 2012 the Court concluded that non-artistic techniques of photographs are not protectable (for example, scanning). See Resolution No 059-2012/TPI-Indecopi and Indecopi (2015), p.75.[49]
- In 2013 Indecopi deduced that a promotional photograph of a model wearing clothes of a textile company does bear originality due to the framing, focus and composition to highlight her outfit. See Resolution No 0384-2013/CDA-INDECOPI, Peruvian Connection Ltd. v SENATI p. 9 and 10.[50]
- In 2021 the criteria for originality of photographs were simplified to three points: transmittable, framed and lighting that shows their personality. Between pages 77 and 82 of this resolution the court evident that press photographs from Hildebrandt en sus trece magazine do carry originality because they focus on the gestures of the photographed and the depth of the camera. See Resolution No 0096-2021/TPI-INDECOPI, Plutón Editores S.A.C. v DP Comunicaciones S.A.C..
Videographic process
There is threshold of originality for audiovisual creations but their protection is similar for both works and recordings (publish/create + 70 years). While cinematographic works ("obra audiovisual") are protected in their entirety, the related rights can only be granted to the producer of non-artistic filming ("grabación audiovisual"),[822/1996 Art. 140] which also include performance and broadcasting.[822/1996 Art. 143] Resolution 000111-1999-ODA-INDECOPI establishes differences between the two terms, in particular, and in a similar way to simple photographs, the fixation of the succession of images. But, Resolution 371-2001/TPI-INDECOPI establishes that the main requirement to receive related rights from the producer of non-artistic filming consists of: "present in their creation process a certain ![]() degree of creativity, technical or organizational skill sufficient to justify the recognition of a similar right in their favor" (p.e. Pay-per-View events).
degree of creativity, technical or organizational skill sufficient to justify the recognition of a similar right in their favor" (p.e. Pay-per-View events).
Theoretically, a security camera captures in a public place could ![]() lack of their producer (as a public asset is mainly assumed to Peruvian State) to be in the public domain. Security camera footage from Sistema Nacional de Seguridad Ciudadana is provided anonymously to the Peruvian National Police or Public Prosecutor's Office like state cameras in public areas, there is no knowed evidence from the original producer of the material.[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 18] Opinión Consultiva 60-2019-JUS/DGTAIPD indicates that footage records are disclosure if these are for public interest and share in open data process (see also Works by the Peruvian Government
),[N° 007-2020-IN Art.22] the places filmed correspond to "places of public domain",[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 7] human monitoring exists but does not interfere with the surveillance camera's technical or creative ability for recording.[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 2] Also it isn't artistic work since its custody cannot be altered from the original,[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 19] as a result, the footage is below the threshold of originality and don't comply with related rights of article 143 of the 1996 law.[51][52] Moral rights prevail of the person involved in this media. For these footage in official works, use {{PD-PE-exempt}}.
lack of their producer (as a public asset is mainly assumed to Peruvian State) to be in the public domain. Security camera footage from Sistema Nacional de Seguridad Ciudadana is provided anonymously to the Peruvian National Police or Public Prosecutor's Office like state cameras in public areas, there is no knowed evidence from the original producer of the material.[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 18] Opinión Consultiva 60-2019-JUS/DGTAIPD indicates that footage records are disclosure if these are for public interest and share in open data process (see also Works by the Peruvian Government
),[N° 007-2020-IN Art.22] the places filmed correspond to "places of public domain",[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 7] human monitoring exists but does not interfere with the surveillance camera's technical or creative ability for recording.[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 2] Also it isn't artistic work since its custody cannot be altered from the original,[N° 007-2020-IN Art. 19] as a result, the footage is below the threshold of originality and don't comply with related rights of article 143 of the 1996 law.[51][52] Moral rights prevail of the person involved in this media. For these footage in official works, use {{PD-PE-exempt}}.
Logos, designs and other works
Simple or ordinary logos and designs are ![]() OK to upload to Commons, because they are below the threshold of originality required for copyright protection. In words of Indecopi and Ministry of Justice and quoting Resolutions No. 1349-2001/TPI-INDECOPI (first paragraph) and 0286-1998/TPI-INDECOPI (second paragraph):
OK to upload to Commons, because they are below the threshold of originality required for copyright protection. In words of Indecopi and Ministry of Justice and quoting Resolutions No. 1349-2001/TPI-INDECOPI (first paragraph) and 0286-1998/TPI-INDECOPI (second paragraph):
| “ | According to Article 3 of Decision 351 [of the Andean Decision], in accordance with Article 2 of Legislative Decree No. 822, a work is understood to be any original intellectual creation of an artistic, scientific or literary nature, susceptible of being disclosed or reproduced in any form.[...] Whatever already part of the cultural heritage -artistic, scientific or literary- will not be considered [original creation], nor will [original] the form of expression that derives from the nature of things or from mechanical-only application of the provisions of certain legal norms, nor will [original] the form of expression that is reduced to a simple technique or simple instructions that only require manual skill for this execution. | ” |
—Indecopi, La originalidad como requisito de protección por derechos de autor ("requisito de la originalidad"), Precedentes y normativa del Indecopi en Propiedad Intelectual (2015)[49] | ||
In 18th paragraph in Casación Número: 1686-2011 explains the use of originality with architectural works satisfying utilitarian functions:
| “ | The originality of the architectural work [...] must be sought essentially in the creative features that are most distinguishable from the purposes of the model, its nature, its geographic and landscape context, and the functional requirements of the costumer, as well as the technical and urban planning standards applicable to the case; and respond rather, in a particular way or as totality, to the individuality or artistic personality of the author. [An] architectural model [...] must be subjected to analysis for the purpose of identifying whether they respond only to elements of functionality or natural characteristics of the species to which they belong or, on the contrary, contain features that correspond to the whim or personality that the author has wanted to attribute to them, beyond their functionality or technical rigor, resulting in giving individuality to the work, in relation to the rest of the constructions of its species. | ” |
-
Telefónica v Deutsche Telekom (Resolución N° 1127-1998/TPI-INDECOPI)[49]: "It's not possible to grant a monopoly on this letter in favour of a single holder".
-
Agrotrade S.R.LTDA. v Infutecsa E.I.R.L. (Resolución Nº 0286-1998/TPI-INDECOPI)[49]: "When it is certain that a creation lacks individuality and has been copied verbatim, it does not make it a work".
-
Resolución Nº 1370-2011/TPI-INDECOPI: "Although it is not a common typeface and may eventually show some differences with respect to the classic graph, this is not sufficient to consider that the work is protected by copyright".
-
Resolución Nº 0366-2011-TPI-INDECOPI: "The title of the poster consists of a sentence without creativity and directly informs and announces the content of the event".
-
Corporación Oro Verde S.A.C. v Industrias Alimenticias Cusco S.A. (Resolución Nº 008-2008/CDA-INDECOPI): "The borders with Inca motifs and the typeface used to represent the word "CUSCO" do not meet the requirement of originality sufficient to be considered an artistic work".
-
Carga Máxima v Del Barrio and Compañía Peruana de Radiodifusión (Resolución Nº 0209-2019/CDA-INDECOPI): the court determined that the "squeaky font style" from Chicha posters for this logo is not original due to its common usage.
-
Resolución N° 0546-2005/TPI-INDECOPI: In the "drawing", they bear the texts and the crown of the Statue of Liberty, which lack individuality.
-
Resolución N° 0698-2014/TPI-INDECOPI: "The fact that [...] the exclamation mark is written in an irregular form and that each letter or sign has a different color, [does not] determine that such characteristics endow the design applied for registration with the features of originality required by the norm to provide it with protection as a work".
-
Resolución Nº 1194-2017/TPI-INDECOPI: "The Court notes that there are no original elements, since they are figures that do not present any particularity, which have been reproduced in the usual manner, without any element having been included".
-
Resolución Nº 1192-2017/TPI-INDECOPI (see Resolución Nº 1194-2017/TPI-INDECOPI).
-
Resolución N° 4301-2015/TPI-INDECOPI: "These are ornamental elements that lack originality, since the same or similar ones are being used by different people and companies to identify".
-
Empresas Luc-Chetti S.A. v Molinoitalia S.A. y Pragma DePublicidad S.A. (Resolución Nº 074-2000/TPI-INDECOPI): "[...] although musical works comprise melody, harmony and rhythm; exclusive rights to the melody can only be acquired".[53]
-
Resolución Nº 211-94-DA-INDECOPI: "la protección [...] no abarca la ordenación alfabética de usuarios que contiene [la guía telefónica]"
-
Resolución N° 0184-2008/TPI-INDECOPI: The miniature representation of Machu Picchu in plastic material cannot be granted as an original work, because its registration would prohibit people create other miniature versions of the citadel.[55]
-
Resolución Nº 1645-2007/TPI-INDECOPI: "The elaboration of a [portable stage] (similar to this image) may have meant an intellectual effort on the part of its creator, but it does not have enough characteristics to be considered a work of [3D] art, since it consists of a simple arrangement of removable panels in the form of a screen".
-
Resolución Nº 0148-2008/TPI-INDECOPI: "However, the Court considers that allowing protection to a design composed exclusively of figures or designs in the public domain, such as the Inca chakana, would mean for no other person to be able to use such designs belonging to the common cultural heritage".
-
Resolución Nº 0083-2011/DDA-INDECOPI does not consider protection to use of Tumi with common text.
-
A newsline that is not subject to copyright protection but the image, also not considered a work of authorship, is subject to related protection for 70 years post-creation.
-
Resolución N° 0082-2023/TPI-INDECOPI: "The additional elements that appear on the images (e.g. rectangles containing phrases or expressions) also do not present particular features that denote a minimum of originality, so they cannot be protected by copyright"
Note: Some creations are above the threshold of originality and ![]() are not valid for upload to Commons:
are not valid for upload to Commons:
- Logo of Tres Olivas: a leaf with three olives with tonalities, use of brightness and sensation of movement. See Resolution No 1774-2012/TPI-INDECOPI, Olivos del Sur S.A.C. vs Antonio Moncayo Cortés.[56]
- Emblema La Primera. See Resolution No 2361-2016/TPI-INDECOPI.
- A fictional character in Superman: Krisis of the Krimson Kryptonite. See Resolution No 1164-2014/TPI-INDECOPI.
- A logo with a people with torch to the letter E, above the letter T. Triunfo Empresarial. See Resolution No 0319-2018/TPI-INDECOPI.
COM:TOO Philippines
Filipíny
The concept of threshold of originality probably does not exist in the Philippines. It is possible that the sweat of the brow concept applies. In this concept, "a work can be eligible for copyright protection if there is a substantial amount of labor, effort, or investment involved, even if it lacks a significant level of creativity. This standard places emphasis on the effort put into creating the work rather than the level of originality or creativity." (Reference: Commons:Village pump/Copyright/Archive/2023/07#Probable low Philippines TOO)
For this reason, some logos that may be simple for the American jurisprudence may be eligible for copyright in the Philippines. Two examples are logos of Photo Sikwate (2022-00957-G) and of Geomax Solutions and Innovations (2022-01698-G), both of which were afforded copyright registration as proven by the 2022 copyright registry of Intellectual Property Office of the Philippines.
However, in the midst of controversy surrounding the most popular noontime variety show of the Philippines in mid-2023 (refer to w:en:Eat Bulaga!#Copyright infringement case for the background information), Atty. Maggie Garduque who represents the show's producer (TAPE, Inc.) claims the design of the logo of the show "is a trademark and not subject of copyright."[57]
COM:TOO Poland
Polsko
Nejsou k dispozici žádné informace
COM:TOO Portugal
Portugalsko
w:File:Juventude Socialista Portugal.png was deleted as it was considered to be above the threshold of originality.
- Photographs
In Portugal photographs have been consistently specifically required to have a significant degree of creativity in order to be copyrighted. Article §164 of the current 2017 copyright law states that "the choice of a photograph's subject and the conditions of its creation must be deemed to be a personal artistic creation by the author before a photograph may qualify for protection".
- Court cases
- Landscape photograph: Ruled as without originality. In 2009 the Tribunal da Relação de Lisboa ruled as void of copyright for lack of artistic creativity a landscape photograph the author was claiming copyright on due to his choice of the setting, light and other conditions. It was considered by the court "a vulgar photograph resultant from the mere choice of an object, such as a city council building and part of a group of trees, without a minimum of creativity".[58] The subject is discussed in a 2017 article published by the Instituto Portugues de Fotografia.[59]
- Heart reproduction commissioned to a laboratory in order to be presented in an exposition: Ruled as without originality.[58]
- Clothing/Fashion: Ruled as without originality.[60]
- Puppets wearing Madeira national costumes (generally tourist souvenirs) following old and common models were considered without copyright.[61]
COM:TOO Russia
Rusko
- Automatic camera works
![]() use {{PD-RU-exempt-autocam}}
use {{PD-RU-exempt-autocam}}
![]() A photowork or a videowork made by automatic camera (Russian: автоматическая камера, not to be confused with automated camera: автоматизированная камера) is not the subject of copyright, because such work is made by technical tool without creative human activity. The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, Part 80 of Session Resolution No. 10 of April 23, 2019 on Application of Part IV of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
A photowork or a videowork made by automatic camera (Russian: автоматическая камера, not to be confused with automated camera: автоматизированная камера) is not the subject of copyright, because such work is made by technical tool without creative human activity. The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, Part 80 of Session Resolution No. 10 of April 23, 2019 on Application of Part IV of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
Examples
- Any photowork or videowork made by automatic camera for administrative violation record (for example, by automatic camera for driving offense record[62]). The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, Part 80 of Session Resolution No. 10 of April 23, 2019 on Application of Part IV of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
- Simple creative works
![]() Simple result of creative work (creative human activity) is copyrightable. The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, Part 80 of Session Resolution No. 10 of April 23, 2019 on Application of Part IV of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
Simple result of creative work (creative human activity) is copyrightable. The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, Part 80 of Session Resolution No. 10 of April 23, 2019 on Application of Part IV of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
Examples
- Simple black square as geometric shape is uncopyrightable as itself. However Black Square by Kazimir Malevich was copyrightable because this painting was the result of creative work in recognized art style - suprematism, and it is in Public Domain because of copyright term expiry, not because of result simplicity.
- Logos
![]() In doubt There is no clear precedent in Russian courts for the threshold of originality for simple logos.
In doubt There is no clear precedent in Russian courts for the threshold of originality for simple logos.
COM:TOO Senegal
Senegal
Works of the mind may enjoy protection only if they are original. "Originality" means the work bears the stamp of the author's personality.[2008-09 Article 7]
COM:TOO Slovenia
Slovinsko
The threshold of originality in Slovenia depends on the field of creativity. If the maneuvering space of the possible creativity is narrower, it requires more creativity for a work to be copyrighted.[63]
In this regard, the following court cases are relevant:
Applied arts:
- VSL0069492 - the design of a couch set has been found to be below the threshold.
- VS0011606 – the design of a sales stand has been found to be above the threshold.
Architecture:
- VSL00432 – only the works that constitute an original artwork are copyrighted; the renovation plan of Ljubljana Castle as well as the newly built and (at least some of) the renovated parts of the castle count as such.
Logo:
- VSL00013281 – the logo with inscription "I Feel Slovenia" [5] was found to constitute a copyrighted work.
- The court opined: "The slogan and the logo, which contains both verbal and graphic elements, do not allow them to be separated. Only the synergy of the verbal and graphic elements allows the observer to identify the overall message of the author's work."
Titles:
- VS07924 – the title "Brez zavor" (meaning "Without inhibitions") has been found to be below the threshold.
COM:TOO South Korea
Jižní Korea
According to a machine translation of the Copyright Act as amended up to Act No. 14634 of March 21, 2017,
- "Work" refers to a creation that expresses human thoughts or feelings.[432/1957–2017 Article 2.2]
The Supreme Court of South Korea declared that it is sufficient to be work if:[64]
- it is not just an imitation,
- it has own characteristics as a product of mental efforts, and
- it can be distinguished from existing ones.
Seoul High Court judged the seagull pattern and the figure of Ebisu of EVISU Japan is not copyrighted because they cannot be recognized for originality.[65] Also, The Supreme Court of South Korea has ruled that typefaces are not copyrighted. (See also Commons:Copyright rules by territory/South Korea § Signatures)
However, the Supreme Court of South Korea judged the logo of Fox Racing is copyrighted.[66]
COM:TOO Spain
Španělsko
STS 4443/2004 notes that a work must have the characteristics of "uniqueness, individuality and distinguishability" to qualify for protection.[67]
STS 1644/2017 concerns architecture and states "The terms in which an architectural project is drawn up largely respond to the technical or functional requirements and compliance with urban regulations. When this is the case, the project or the architectural buildings are not protected by copyright in the part imposed by those technical, functional or normative requirements"; and more generally, "the factor of recognizability or differentiation of the work with respect to the pre-existing ones [is] essential to grant an exclusive right with moral and patrimonial aspects".[68]
COM:TOO Sweden
Švédsko
"A simple general rule is that if it is unlikely that two persons would create, for example, a text identically or similarly, the text is probably sufficiently original to qualify as a protected work. (..) Often, the requirements for copyright protection are considered to be relatively low."[69] From the court cases below it can be concluded that the threshold of originality in Sweden is significantly higher then the ditto in the United Kingdom even though it might be considered low compared to the one in the United States.
| Status | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|
 |
The text itself can't be considered to fulfill the general threshold of originality considered for copyright protection. This same interpretation is made whether one sees it as Roman numerals or Latin letters. The logo itself does have some figurative design. The font must however, despite some inconsistancies along the edges, be considered as ordinary and the black rectangle in the background does not contribute to any distinctive character. - Patent- och registreringsverket (Swedish Intellectual Property Office) Invändningsärende nr 2017/00120/01, Registrering nr 540495 | |
 |
The logo consists of an a and a 6. The round part of each character is not closed, however the characters are, besides that, made in a fairly ordinary font without any distinctive character. Between the characters is a simple, sun-feather resembelling, figure with a pointy tip which goes down between the characters. Above this figure there are four points, two to the left and two to the right. The logo is way to simple to be granted such copyright protection which can constitute an impediment for others' trademark registration. - Patent- och registreringsverket (Swedish Intellectual Property Office) Invändningsärende nr 2005/0006/0001, Registrering nr 369154.
This ruling was appealed to Patentbesvärsrätten (Patent court of appeals) which settled the original ruling (Mål nr 06-304, vm.reg. 369.154), albeit with one member of the court with a dissenting opinion. Unfortunately, they did not elaborate as to why they settled the original ruling. | |
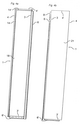 |
Technical drawing. According to decision by the Swedish Supreme Court.NJA 2004 s. 149 | |
| https://shop.textalk.se/shop/4541/files/entombed/ENT_logo_web.png | The logo has been created using a Gothic font in a way which is frequently used among bands in the genre in question [death metal]. The logotype can thus not be considered to fulfill the demands of originality and distinctive character needed for copyright protection. - Patent- och registreringsverket (Swedish Intellectual Property Office) Invändningsärende 2013/0133/0001, Registrering nr 514059.
According to the court, after a comprehensive assessment, the wordmark shows such level of indivudual, distinctive character that it must be considered to possess copyright protection. The court especially values the font of choice, the individual design of the first and last letter and the fact that the first and last letter has been written in caps. - Patent- och marknadsdomstolen (Patent and Market Court) PMÄ 10796-16 This ruling was appealed to Patent- och marknadsöverdomstolen (Patent and Market Court of Appeals) which settled the previous ruling (Mål nr PMÖÄ 5441-17). Unfortunately, they did not elaborate as to why they settled the previous ruling. | |
| A black-and-white version of fr:File:Dunderklumpen Logo.png | Ruled above the TOO by Patent- och registreringsverket (Swedish Intellectual Property Office) (Varumärkesansökan nr 2014/00870), another part of the same ruling was appealed to the Patent- och marknadsdomstolen (Patent and Market Court) which settled the original ruling (Mål nr PMÄ 10748-16). Neither instance elaborated further as why the logo was ruled above the TOO but one can speculate that it was because it was a very obvious case. | |
| Michelin man lamp | Ruled above the TOO by Patent- och registreringsverket (Swedish Intellectual Property Office) (Varumärkesansökan nr 2015/03538). The office did not elaborate further as why the logo was ruled above the TOO but one can speculate that it was because it was a very obvious case. | |
 |
Mini Maglite torch (Mål: T 1421-07, Högsta domstolen) | |
| Porcelain [6] | "Sundborn", made by Rörstrand | |
| Photo illustrating a newspaper article | RH 2009:18 (removed from the website in 2004 because of copyright infringement, protected as a photographic work for 70 years after author's death) | |
| Knitted tunic | (NJA 1995 s. 164) | |
| Technical drawings | (NJA 1998 s. 563) |
COM:TOO Switzerland
Švýcarsko
Swiss copyright law defines works as "literary and artistic intellectual creations with individual character, irrespective of their value or purpose".[70] Such works are protected by copyright: "Up to 70 years after the death of the author (50 years for computer programs); 50 years from the taking of a photograph without individual character; 70 years from the performance/publication of a phonogram or audio-visual fixation; 50 years from the transmission of a broadcast."[71] This section discusses some types of subject matter.
Photographs: Photographs may be protected as works on the basis of their individual character (individual photographs). Some photographs that lack individual character may also enjoy protection (non-individual photographs).
- Individual photographs: The individual character may manifest itself in a variety of ways, such as the choice of the depicted object, the decision on when the picture is taken, or the editing work done after the picture has been taken.[72] In a 2003 decision, the Federal Supreme Court of Switzerland held that a photo of Bob Marley taken at a concert by a spectator with a handheld camera was eligible for protection as a photographic work because it had the required individual character by virtue of the aesthetic appeal of the picture, combined with the orientation of the picture's components and the distribution of light and shadow. It also found that the photograph was a "creation of the mind" by being shot at a specific time during the singer's movement on the stage.[73] By contrast, in the 2004 case Blau Guggenheim v. British Broadcasting Corporation, the Court found that a photo (en:File:Christoph Meili 1997-nonfree.jpg), shot by a reporter to document Christoph Meili with the files he had taken from his employer, lacked individual character. It found that the scope of conceptual and technical possibilities was not exploited, and that the photograph did not distinguish itself in any way from what was common use.[74] The copyright in an individual photograph lasts for 70 years from the end of the calendar year in which the author died.[75]
- Non-individual photographs: Effective 1 April 2020, Swiss law also protects certain non-individual photographs. Article 2(3bis) URG provides that "photographic depictions and depictions of three-dimensional objects produced by a process similar to that of photography are considered works, even if they do not have individual character". While no individuality is required, according to the official motives accompanying the (eventually adopted) revision draft, these photographs are still required to be "based on human actions", and thus "automatically created photographs such as radar pictures, pictures from surveillance cameras or camera traps" are ineligible for protection.[76] It should be noted that the new right also applies to photographs created before 1 April 2020 that had previously not been protected for failing the individuality test; however, if a particular use of a non-individual photograph was "begun prior to the commencement" of the new law, it "may be completed".[77] According to the official motives, this has the effect that "if non-individual photographs are used on a web page, the web page may be maintained after the entry into force of the protection of non-individual photographs. If, on the other hand, such photographs are included into an existing or a new web page after the entry into force of this protection, permission is required from the owner of the rights in the non-individual photographs."[78] The copyright in a non-individual photograph lasts for 50 years from the end of the calendar year in which the photo was taken.[79]
COM:TOO Taiwan
Tchaj-wan
The level required for copyright is low. Independently created works with "minimal creativity" are eligible, according to Taiwan's Intellectual Property Office.[80]
The following examples are ![]() :
:
- These two artworks with traditional design elements are unprotected, according to court decisions that they do not meet the originality threshold for copyright protection:[81]
- Simple typeface, such as the typeface of Sunshow company logo:
The following examples are ![]() :
:
- Calligraphy works, including:
- "燒烤飯糰" on this photo, is copyright protected ruled by a court.[82][83]
- "風月堂" (see the last page of the PDF document for the work in question).[84]
- The graphic part of Sunshow company's logo. The court ruled that the graphic part of the logo: two hands clasped together, one over the other, is copyrightable, but the typeface "SUNSHOW" is not.[85]
- The Louis Vuitton Monogram Multicolor pattern [7][86].
COM:TOO Turkey
Turecko
Might be ![]() OK
OK
The Turkish copyright laws depend on the work bearing the characteristics of its creator while deciding whether the work is original, and considered on a case-by-case basis.[87]
Země s běžnými zákony
Země s běžnými zákony běžne používají test „umu a práce“ k posouzení minimální hladiny originality, která je schopna učinit výtvor autorky chráněným. V některých zemích, jako je například Austrálie a Spojené království, je taková hladina extrémně nízká. Nicmoně, Kanada a Indie jsou dvě zásadní výjimky. Bez určité rešerše jednotlivých zákonů nelze usoudit, že textové logo ze země s běžnými zákony je nutně na Commons povoleno. Pokud je zde skutečná pochybnost o pozici, kterou by místní soud mohl zaujmout, potom musí být obrázek smazán na základně Template:PgCommons:Project scope/Precautionary principle.
Pokud je logo extrémně jednoduchá (např. v běžném písmu), není způsobilé k ochraně autorským právem dokonce i v zemích s běžnými zákony.
Pokud víte o specifickém případu zákona či právní rady o této problematice v jakékoliv zemi, prosíme, přidejte sekci „Hranice originality“ do příslušné podstránky země v Commons:Autorská práva podle oblastí a přidejte odkaz do příspěvku níže.
COM:TOO Australia
Austrálie
Nejsou k dispozici žádné informace
COM:TOO Canada
Kanada
Unlike other common law countries, Canada's threshold of originality veers closer to that of the United States. CCH Canadian Ltd. v. Law Society of Upper Canada explicitly rejected the "sweat of the brow" doctrine for being too low of a standard, but at the same time, stated that the creativity standards for originality were too high:
A creativity standard implies that something must be novel or non-obvious — concepts more properly associated with patent law than copyright law. And for these reasons, I conclude that an “original” work under the Copyright Act is one that originates from an author and is not copied from another work. That alone, however, is not sufficient to find that something is original. In addition, an original work must be the product of an author’s exercise of skill and judgment. The exercise of skill and judgment required to produce the work must not be so trivial that it could be characterized as a purely mechanical exercise."
The same case also stated:
For a work to be “original” within the meaning of the Copyright Act, it must be more than a mere copy of another work. At the same time, it need not be creative, in the sense of being novel or unique. What is required to attract copyright protection in the expression of an idea is an exercise of skill and judgment. By skill, I mean the use of one’s knowledge, developed aptitude or practised ability in producing the work. By judgment, I mean the use of one’s capacity for discernment or ability to form an opinion or evaluation by comparing different possible options in producing the work. This exercise of skill and judgment will necessarily involve intellectual effort.
COM:TOO Hong Kong
Hongkong
![]() for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection is presumably very low.
for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection is presumably very low.
Because Hong Kong was a territory of the United Kingdom until 1997, Hong Kong law is modeled on UK law, and in the absence of any specific case law to the contrary it is reasonable to assume that the rules will be similar. See the United Kingdom for more details.
COM:TOO India
Indie
India seems to have a similar threshold of originality as the US Courts, called Modicum of Creativity. Older cases may have similar thresholds of originality to the UK Courts called Sweat of the brow but this is no longer applied.
Robbin Singh has written an essay on the subject that may be useful.[88]
COM:TOO Ireland
Irsko
![]() Unknown
Unknown
Despite uncertainty on the required level of originality needed to qualify for copyright protection, images that have been retained on Commons include:
| Image | Description | Discussion |
|---|---|---|

|
ISPCA official logo | Commons:Deletion requests/File:ISPCA official logo.png |
COM:TOO Israel
Izrael
Although Israel historically used a "skill and labour" test similar to that used by the UK, since the 1989 Israeli Supreme Court's ruling in Interlego A/S v. Exin-Lines Bros. SA they have tended fairly close to a US-style requirement equating originality with human creativity.[89]
In Israel, the Supreme Court in the Interlego A/S v. Exin-Lines Bros. SA decision adopted the Feist ruling with regards to both the interpretation of the originality requirement and the general rejection of the ‘sweat of the brow’ doctrine and the labour theory as a legitimate interest for establishing a copyright claim.
COM:TOO Malaysia
Malajsie
The threshold of originality situation in Malaysia remains ![]() Unsure. Some previous discussions:
Unsure. Some previous discussions:
- The File:Hcc.png was deleted probably based on calligraphic Chinese words, and cited that COM:TOO UK may also applied for deletion;
- But the File:Petronas Logo.svg was nominated and decided to keep twice, despite that this may also beyond COM:TOO UK. Note that this logo is used before June 2013, and since that, the Petronas modified their logo to be more modern and fairly complex, the current Petronas logo is located at English Wikipedia for Fair use, though some users oppose that.
COM:TOO Nigeria
Nigérie
Under the Copyright Act of 1988 (Chapter C.28, as codified 2004), A literary, musical or artistic work shall not be eligible for copyright unless (a) sufficient effort has been expended on making the work to give it an original character;...[C28/2004 Section 1(2)]
COM:TOO New Zealand
Nový Zéland
As stated in the New Zealand government's NZGOAL copyright guide (January 2015),
- As the Court of Appeal has stated, the “threshold test for originality is not high”, the determining factor being “whether sufficient time, skill, labour, or judgment has been expended in producing the work”. The Court has also reiterated the axiom, or principle, that copyright is not concerned with the originality of ideas but with the form of their expression. A work is not original, however, if (a) it is, or to the extent that it is, a copy of another work; or (b) it infringes the copyright in, or to the extent that it infringes the copyright in, another work.[90]
COM:TOO Singapore
Singapur
- For logos
![]() Likely not OK for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection is presumably very low.
Likely not OK for most logos. The level of originality required for copyright protection is presumably very low.
Because Singapore was a territory of the United Kingdom until 1963, Singapore law is modeled on UK law, and in the absence of any specific case law to the contrary it is reasonable to assume that the rules will be similar. See the United Kingdom for more details.
- For buildings
Assume all Singaporean buildings as copyrighted, regardless of design or artistry involved. Copyright Act 2021 (Act 22 of 2021) explicitly considers all buildings as artistic works: a building or a model of a building (whether the building or model is of artistic quality or not).[22/2021 Section 20(1)(a)(ii)] Please use {{FoP-Singapore}} even to plain-looking Singaporean buildings instead of {{PD-structure|SGP}}.
COM:TOO United Kingdom
Spojené království
Nejsou k dispozici žádné informace
Loga a vlajky
- Loga v těchto obrázcích *nejsou* způsobilé ochrany autorským zákonem
-
bylo řečeno, že nesplňuje hranici originality
-
bylo řečeno, že nesplňuje hranici originality
-
(ŽoS)
-
(ŽoS) „PD-textlogo -- bez komentáře“
-
(ŽoS loga australské firmy) „PD-textlogo“
-
(ŽoS loga kanadské firmy) „PD-textlogo“
-
(ŽoS)
-
(ŽoS)
-
(ŽoS)
-
(ŽoS)
- File:Hercules 1998 Intertitle.png původně „pozadí není složité či způsobilé pro jakýkoliv typ autorské ochrany“ (rozhodnuto zde v roce 2010), smazáno v roce 2012, neboť „ukazuje dílo nad hranici originality“.
Architektura
Obrázky, které zde zůstaly, protože postádají originalitu nebo pravidlo de minimis:
Poznámka: některé z těchto rozhodnutí byly kontroverzní.
Fotografie
Fotografie, které byly rozhodnuty nezpůsobilé autorské ochrany:
-
(ŽoS) Fotografie trojrozměrného objektu (držák šuplíku) s křivkami a stíny
-
(DR) Photograph of a three-dimensional object (drawer pull) with bevels and cast shadows
Mapy
Mapy, které byly rozhodnuty nezpůsobilé po autorskou ochranu:

Darden vs. Peters: přidání „výběru písma a barvy, visuálního efektu, jako například reliéf, stínování, popisků a výzev“ a vyhlazené do již existující mapy je pod hranicí originality
Použití: Template:TlPD-map. Viz sekci níže ohledně částnečného kopírování či ořezu prvků nezpůsobilých ochrany autorským zákonem z obsahu autorsky chráněného.

Darden v. Peters: the addition of "font and color selection; visual effects such as relief, shadowing, and shading; labeling; call-outs" and anti-aliasing to a preexisting map is below the threshold of originality
Use: {{PD-map}}. See the section farther down on partial copying or cropping of uncopyrightable elements from copyrighted works. Viz též:
- Commons:Map resources a sekce ohledně map pro volné užití na webu.
- Wiki Open.Michigan. Archiv judikátu o tom, „zda je předmět obsahu chráněn autorským právem USA, či nikoliv“.. Začátek v sekci map. Zejména mapy tvořené daty jsou pro volné užití. Mapa reprezentuje data. Všechna rozhodnutí v tvorbě mapy jsou založena na utilizaci a informačního rozhodování. Viz též: Commons talk:Threshold of originality#Casebook. More locations. Viz tento archiv jurisdikátu univerzity v Michiganu zde. Načítá se mnohem rychleji než jurisdikát na archive.org.
- Mapy pro volné užití. Z: Public Domain Sherpa. Právník se zaměřením na autorské právo a ochranné obchodní známky.
- Category:PD map
Grafy
Grafy, které byly rozhodnuty jako nezpůsobilé autorské ochrany. Použití: {{PD-chart}}. Viz sekce níž na částečném kopírování či ořezu nechráněných částí z autorsky chráněných děl. Viz též:
- Commons:Chart and graph resources a sekce ohledně volného užití grafů na internetu.
- Open.Michigan Wiki. Casebook archive on "whether or not the content object is protected by US Copyright law.". Začátek v sekci grafů. Viz též: Commons talk:Threshold of originality#Casebook. More locations. Viz archiv tohoto přehledu případů michiganské univerzity zde. Načítá se mnohem rychleji než přehled na archive.org.
- Category:PD chart
-
Viz diskuse.
-
Viz info v sekci autora v popisu souboru.
-
Viz žádost o smazání, a tuto diskusi.
-
Viz žádost o smazání.
-
Viz žádost o smazání.
-
See the info in the author section of the file description.
-
See the deletion discussion, and this discussion.
-
See the deletion discussion.
-
See the deletion discussion.
Částečné kopírování nebo ořez autorsky chráněných děl
Pokud soubor kopíruje pouze část autorsky chráněného díla, status autorské ochrany je rozhodován pouze na základě toho, co bylo zkopírováno. Pokud soubor obsahuje pouze prvky, které nelze autorsky chránit, pak tento soubor též nelze autorsky chránit. Jinými slovy posuzujeme status autorskoprávní ochrany souboru pouze na základě obsahu tohoto souboru, nikoliv na základě obsahu původního zdroje, který nebyl zkopírován.
 |
Tento obrázek předního přebalu románu je v USA volně k užití, protože pouze kopíruje text, který nelze autorskoprávně chránit, obsah knihy samotné, který nelze autorskoprávně chránit nebo možná autorskoprávně ochranitelný obsah zadního přebalu. (ŽoS) Nejspíše by soubor nebyl volně k užití ve Spojeném království, protože písmo britského vydavatele má autorskoprávní ochranu na 25 let, avšak je faktem, že toto typografické uskupení bylo zveřejněno před více než 25 lety. |
Nižší hranice ve Spojeném království, atd.
- File:BBC.svg a další přidružené varianty pro divize BBC byly ponechány, protože pouze obsahují Gill Sans, který je starým standardním písmem.
Viz Commons:Deletion requests/File:BBC.svg. - File:Clerical Medical.png (nahráno jako nesvobodný obsah (fair use) na en.wikipedia.org)
Viz Commons:Deletion requests/File:Clerical Medical.png (s odůvodněním loga EDGE).
Viz též
- Šablona {{Licensed-TOO}} pro formátování a překlad licencí obrázku TOO
- Commons:Copyright rules by subject matter
- Category:Threshold of originality related deletion requests
- Commons:When to use the PD-scan tag - ohledně úrovně originality naskenovaného díla potřebné pro generaci autorskoprávní ochrany nezávislé na daném díle
- Commons:When to use the PD-Art tag - ohledně úrovně originality fotografie díla potřebné pro generaci autorskoprávní ochrany nezávislé na daném díle
- meta:Wikilegal/Copyright threshold of originality for logos
- Category: PD-ineligible license tags
- Category: PD ineligible
- Commons:Chart and graph resources. Včetně ostatních zdrojů pro volné užití.
- Commons:Map resources. Včetně ostatních zdrojů pro volné užití.
Reference
| Some citation text may not have been transcluded |
|---|
|
Pro více kompletní a funkční reference viz Commons:Autorská práva podle oblastí a individuální kategorie a oblasti:




_Nettivihje_logo.gif/80px-Pelastakaa_Lapset_(Save_the_Children_Fund)_Nettivihje_logo.gif)

.gif/80px-K-Plussa_logo_(old).gif)



.svg/87px-Inter_Old_Logo_(2007-2014).svg.png)




.png/86px-Inca_Kola_Advertisement_Hartog_Bell_(cropped).png)

![Telefónica v Deutsche Telekom (Resolución N° 1127-1998/TPI-INDECOPI)[49]: "It's not possible to grant a monopoly on this letter in favour of a single holder".](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ad/Telefonica_1984.png/120px-Telefonica_1984.png)
![Agrotrade S.R.LTDA. v Infutecsa E.I.R.L. (Resolución Nº 0286-1998/TPI-INDECOPI)[49]: "When it is certain that a creation lacks individuality and has been copied verbatim, it does not make it a work".](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d3/Label_VECCYPER_in_Resolución_Nº_0286-1998%2C_Indecopi.png/97px-Label_VECCYPER_in_Resolución_Nº_0286-1998%2C_Indecopi.png)



![Empresas Luc-Chetti S.A. v Molinoitalia S.A. y Pragma DePublicidad S.A. (Resolución Nº 074-2000/TPI-INDECOPI): "[...] although musical works comprise melody, harmony and rhythm; exclusive rights to the melody can only be acquired".[53]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e2/5as_e_8as_diretas_permitidas_nas_partes_intermediárias_-_quinta_em_parte_extrema.png/120px-5as_e_8as_diretas_permitidas_nas_partes_intermediárias_-_quinta_em_parte_extrema.png)
![Resolución Nº 211-94-DA-INDECOPI: "la protección [...] no abarca la ordenación alfabética de usuarios que contiene [la guía telefónica]"](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/86/Annuaire.jpg/120px-Annuaire.jpg)
![Far from fiction, Duff is an element that individually lacks the protection of a work of art. Subsequently, Fox managed to obtain identification characteristics to be registered as beer trademark (Resolución Nº 1508-2009/TPI-INDECOPI).[54]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/21/The_Simpsons_Duff_Beer.jpg/120px-The_Simpsons_Duff_Beer.jpg)
![Resolución N° 2418-2009/TPI-INDECOPI: While the angle of the handle to the horizontal line or the depth of the concave part of the teaspoon [is slightly different] from the standard shape [...] the object is not an original work, due to the common form of others teaspoons.[55]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f0/Cucharadita_de_té_(in_Resolution_2418-2009).png/107px-Cucharadita_de_té_(in_Resolution_2418-2009).png)
![Resolución N° 0184-2008/TPI-INDECOPI: The miniature representation of Machu Picchu in plastic material cannot be granted as an original work, because its registration would prohibit people create other miniature versions of the citadel.[55]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/eb/Machu_Picchu%2C_Peru.jpg/120px-Machu_Picchu%2C_Peru.jpg)
![Resolución Nº 1645-2007/TPI-INDECOPI: "The elaboration of a [portable stage] (similar to this image) may have meant an intellectual effort on the part of its creator, but it does not have enough characteristics to be considered a work of [3D] art, since it consists of a simple arrangement of removable panels in the form of a screen".](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/db/Screen_(PSF).png/120px-Screen_(PSF).png)











.svg/120px-Logo_of_the_LG_Corporation_(1995-2014).svg.png)












